Solar energy is often hailed as the green solution to our energy woes, but it’s not without its own environmental pitfalls. Are we overlooking the hidden costs of going solar? Here are 20 points that shed light on the darker side of solar power.
1. Manufacturing Emissions

Producing solar panels is an energy-intensive process. Manufacturing one ton of polysilicon, a key component in solar panels, releases about 3-4 tons of CO2 into the atmosphere.
2. Toxic Chemicals

Solar panel production involves hazardous chemicals like cadmium and lead. These substances can cause serious environmental harm if not properly managed.
3. Water Usage

The production process of solar panels requires substantial water use. For instance, producing a single solar panel can consume up to 1,400 liters of water.
4. Mining Impact
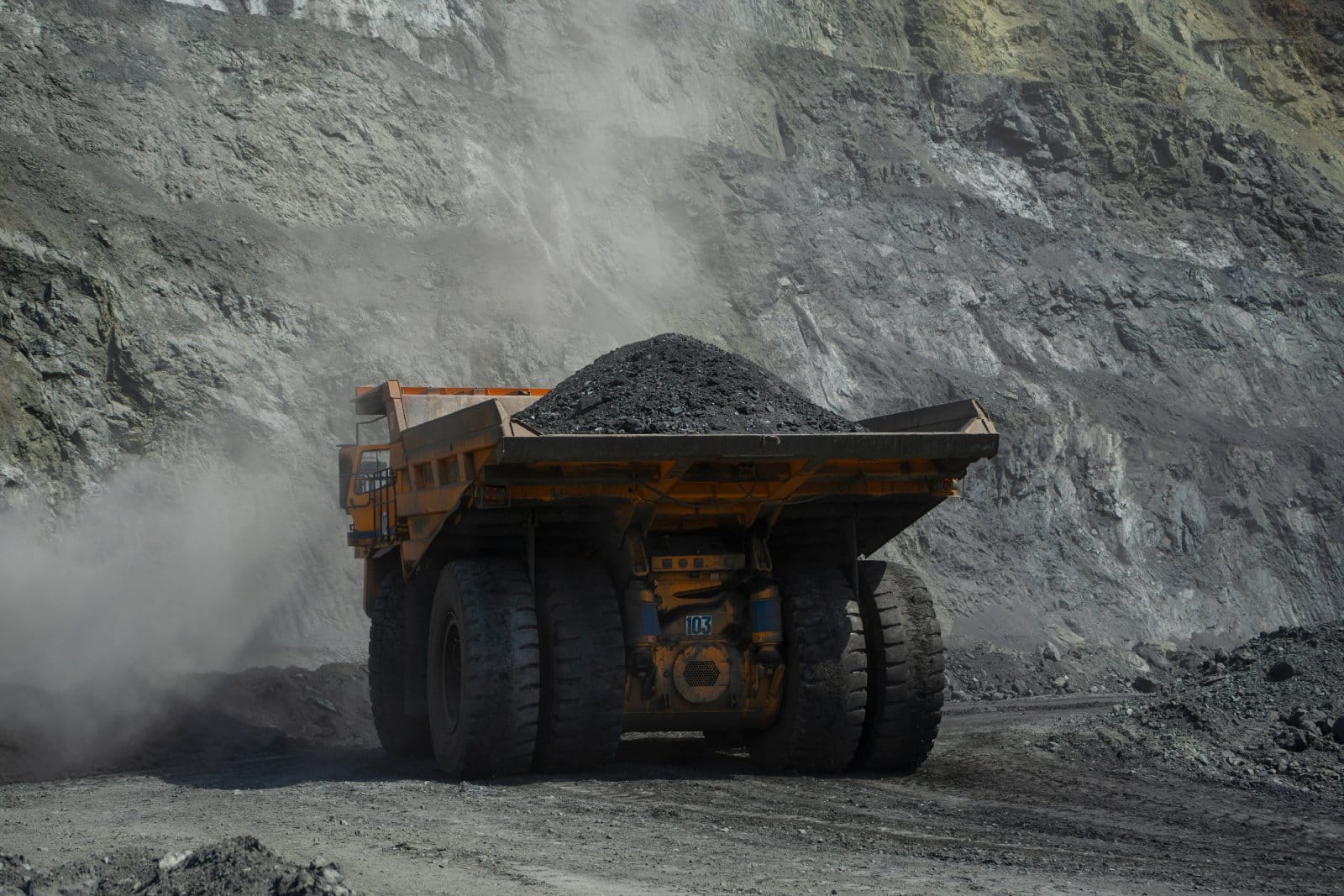

Mining for materials like silicon, copper, and rare earth elements required for solar panels can lead to land degradation and water pollution.
5. End-of-Life Disposal

Disposing of old solar panels is a significant issue. With a lifespan of about 25-30 years, many panels are nearing their end, creating a new wave of electronic waste.
6. Recycling Challenges

Recycling solar panels is not straightforward. The process is costly and complex, with less than 10% of panels currently being recycled.
7. Land Use
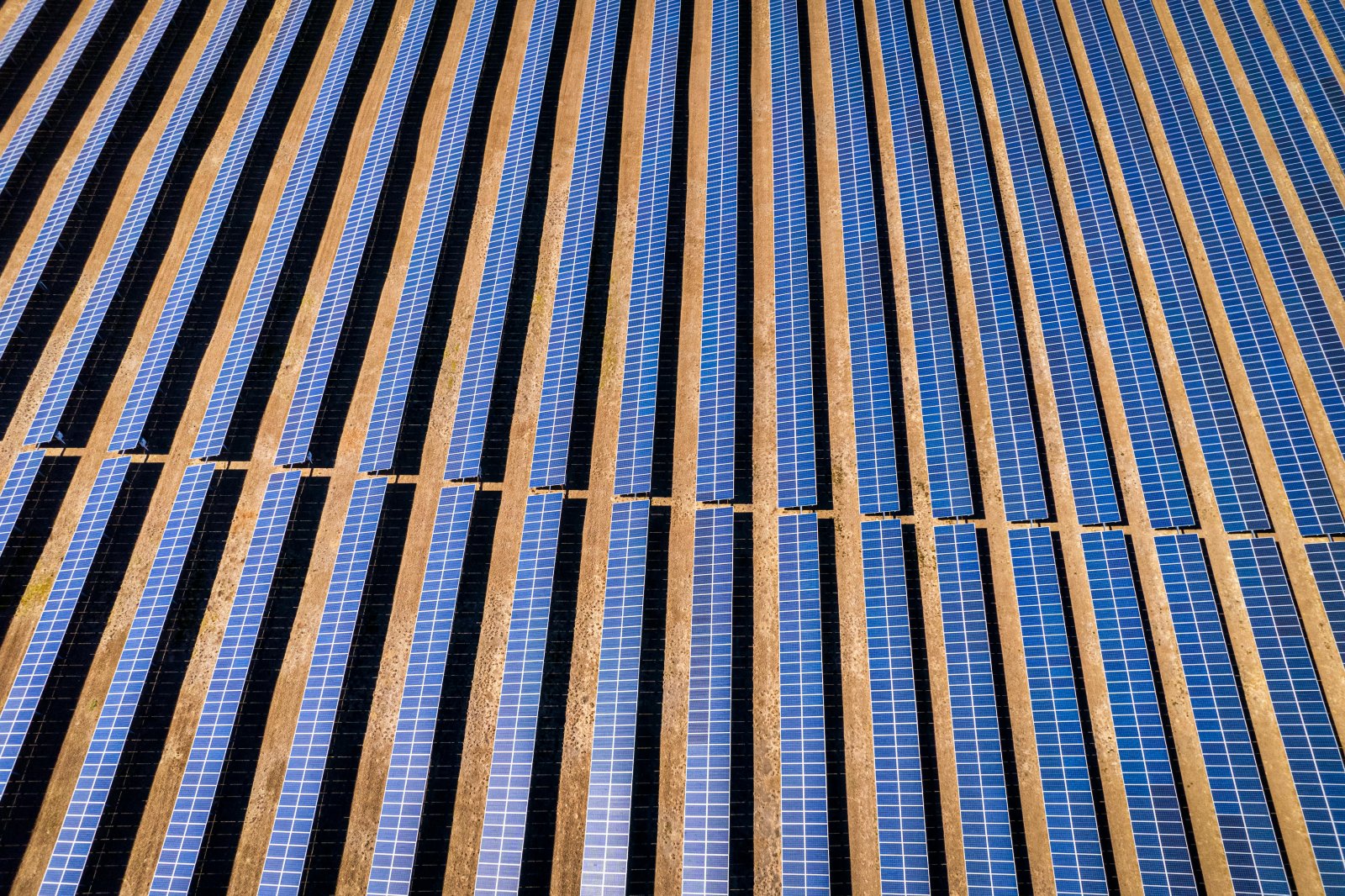

Large solar farms require significant land, potentially leading to habitat destruction. The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System, for example, spans over 3,500 acres in the Mojave Desert.
8. Energy Payback Time

It takes several years for a solar panel to generate the amount of energy that went into making it. This energy payback time can range from 1 to 4 years depending on the technology and location.
9. Resource Scarcity

Key materials for solar panels, such as indium and tellurium, are becoming increasingly scarce. This scarcity could drive up prices and create supply chain issues.
10. Human Rights Concerns

The mining of materials for solar panels often occurs in regions with poor labor practices. Reports of child labor and unsafe working conditions are common in cobalt mines in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
11. Energy Storage Problems

Solar power is intermittent, requiring efficient storage solutions. Current battery technologies, like lithium-ion, have their own environmental and ethical issues.
12. Carbon Footprint of Installation

Transporting and installing solar panels involves fossil fuel use, contributing to their overall carbon footprint.
13. Wildlife Disruption
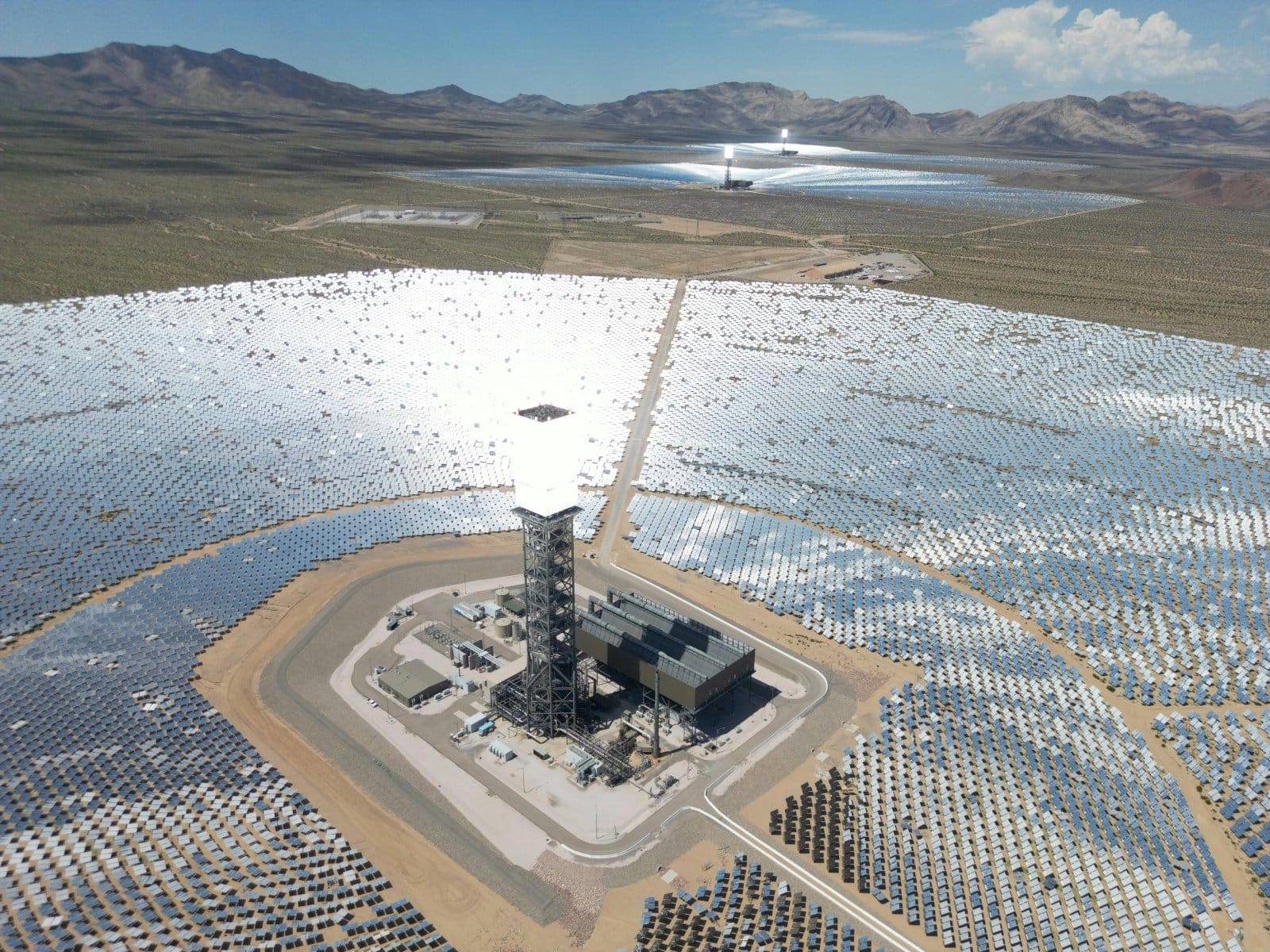

Solar farms can disrupt local wildlife. For example, the Ivanpah solar plant has been linked to the deaths of numerous birds and other wildlife.
14. Efficiency Losses

Solar panels degrade over time, losing efficiency. After 20 years, a panel may only produce around 80% of its original power output.
15. Economic Inequity

The high upfront cost of solar installations means they are often accessible only to wealthier households, leaving low-income families behind in the green energy transition.
16. Subsidy Dependence

The solar industry relies heavily on government subsidies. Without these, the financial viability of solar power could be severely compromised.
17. Grid Integration Issues

Integrating solar power into existing electrical grids can be challenging and expensive, often requiring significant infrastructure upgrades.
18. Seasonal and Weather Dependence

Solar energy production is highly dependent on weather and seasons, making it less reliable in regions with less sunlight.
19. Visual Impact
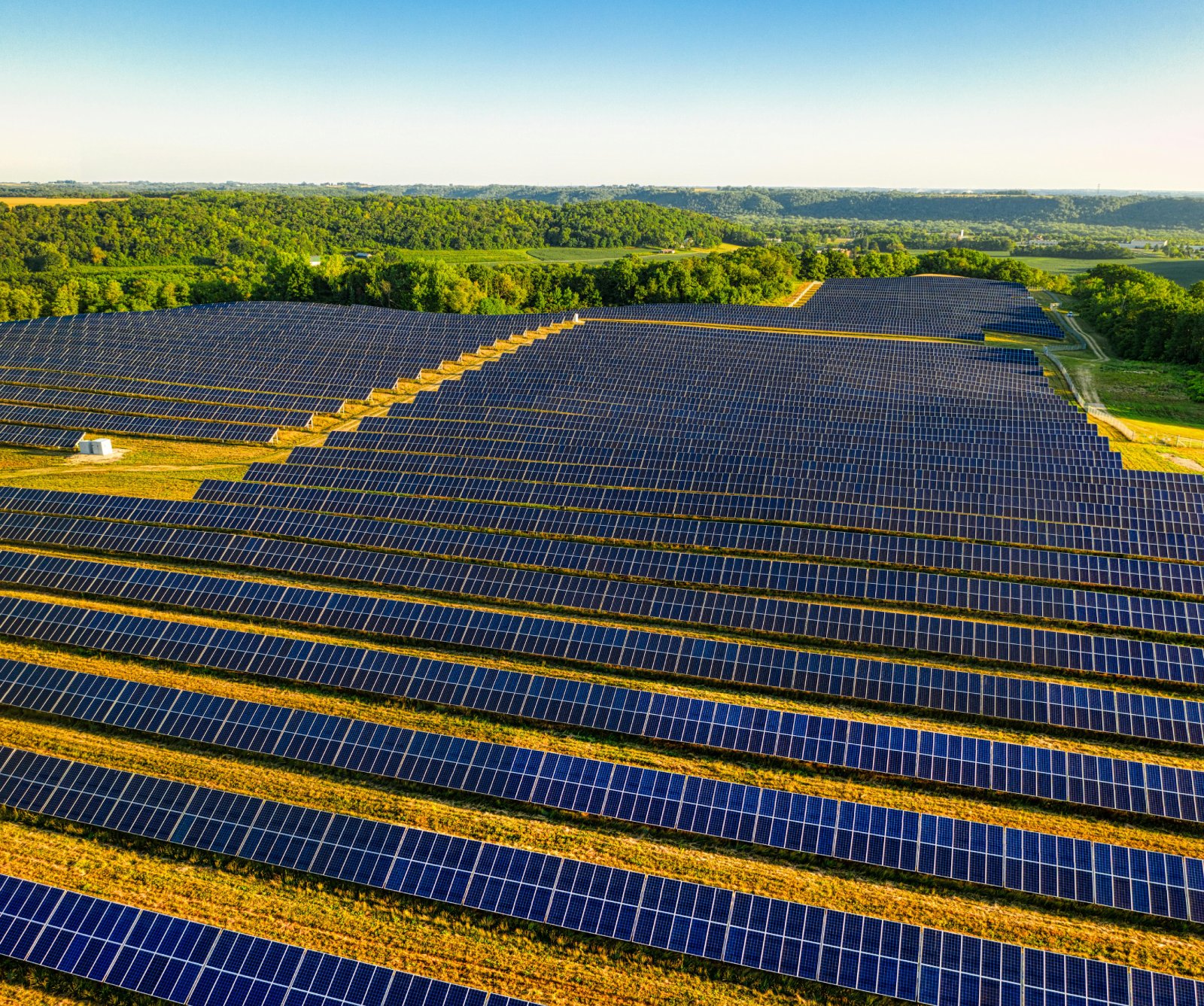

Large solar farms can alter landscapes and may face opposition from local communities due to their visual impact.
20. Long-Term Waste Management

There is currently no comprehensive plan for managing solar panel waste on a large scale, posing a future environmental challenge.
The Green Dilemma

While solar energy offers a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, it’s not without its environmental costs. As we push for a greener future, it’s crucial to address these challenges head-on. Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of solar power will help us make more informed, sustainable choices. Are we ready to confront the dark side of our bright future?
Remote No More: 19 Companies Returning to the Office

As the pandemic wanes, companies are recalling remote workers back to the office, sparking debates on fairness, costs, and convenience. However, there are also notable productivity, coworking, and mental health benefits to consider. Feeling the effects of these changes? Remote No More: 19 Companies Returning to the Office
8 Costco Must Buys and 8 to Leave Behind

Ever wandered Costco’s aisles, questioning if that giant jar of pickles is a real bargain? Or debated buying tires where you get your rotisserie chicken? Welcome to the definitive guide to Costco shopping—a journey to save money, prevent regrets, and offer quirky insights into bulk buying. 8 Costco Must Buys and 8 to Leave Behind
23 Reasons Texas Is the Next Big Thing

Texas is becoming a beacon of opportunity, blending cultural heritage with economic growth. From its landscapes to its industries, the Lone Star State offers a dynamic lifestyle. Here are 23 reasons why Texas stands out, attracting entrepreneurs, artists, tech professionals, and families seeking new beginnings. 23 Reasons Texas Is the Next Big Thing
The post Solar Power’s Dirty Secrets: 20 Hidden Environmental Costs You Need to Know first appeared on Career Step Up.
Featured Image Credit: Pexels / Magic K.
The content of this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute or replace professional financial advice.
For transparency, this content was partly developed with AI assistance and carefully curated by an experienced editor to be informative and ensure accuracy.